HTML 5 & Semantic Elements
Overview
In programming, semantic mark-up refers to the meaning of a piece of content — for example “what effect does running that line of JavaScript have?”, or “what purpose or role does that HTML element have” (rather than “what does it look like?”.)
A semantic element clearly describes its meaning to both the browser and the developer.
Examples of non-semantic elements: <div> and <span> – Tells nothing about its content.
Examples of semantic elements: <form>, <table>, and <article> – Clearly defines its content.
For example, the <h1> element is a semantic element, which gives the text it wraps around the role (or meaning) of “a top level heading on your page.”
By default, it will be given a large font size to make it look like a heading (although you could style it to look like anything you wanted), but more importantly its semantic value will be used in multiple ways, for example search engines will consider its contents as important keywords to influence the page’s search rankings (see SEO), and screen readers can use it as a signpost to help visually impaired users navigate a page.
On the other hand, you could make any element look like a top level heading. Consider the following:
This will render to look like a top level heading, but it has no semantic value, so it will not get any extra benefits as described above. It is therefore a good idea to use the right HTML element for the right job.
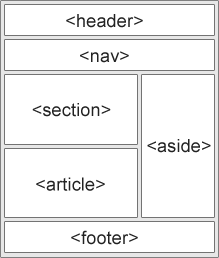
Many web sites contain HTML code like: <div id=”nav”> <div class=”header”> <div id=”footer”> to indicate navigation, header, and footer.
HTML5 offers new semantic elements to define different parts of a web page:
|
 |
Things To Know
- In programming, semantics refers to the meaning of a piece of code.
- The basic semantic elements and what they do.
- Understand that search engines consider semantic elements contents as important keywords to influence the page’s search rankings.
- A semantic element clearly describes its meaning to both the browser and the developer.
- Semantics is the study of the meanings of words and phrases in a language.
- Semantic elements = elements with a meaning.
- Identify semantic elements.